Treatment of low sperm count is possible with custom-made Homeopathy medicines from Welling Homeopathy Clinics, the leading speciality fertility clinic of India.
Welling Homeopathy Treatment offers speciality Homeopathic medicines for the treatment of Oligospermia helping men to father a child at the earliest. Our treatment can help as a stand-alone treatment to increase sperm count or as a pre-IVF treatment to improve the sperm count, motility and morphology.
Call +91 8080 850950 to book an appointment with our specialist or order online instantly from the link above.
How Our Homeopathy Medicines Increase Sperm Count Fast?
First step is to talk to our specialist to understand how our Homeopathy medicine formula can increase your sperm count fast. You should then start Welling Homeopathy treatment, because we are
- First and the largest Homeopathic infertility Clinic in the world with satisfied patients from 108 countries,
- The custom-made Homeopathy medicines for low sperm count has been effective over the last 18 years,
- The Homeopathy treatment for low sperm count is non-hormonal and side-effects free,
- The treatment has a success rate of 65% in the first treatment cycle of 6 months,
- The treatment has already helped over 7500 men from 108 countries and can help you too.
Call +91 8080 850950 to book an appointment with our specialist or order online instantly from the link above.
Consult our specialists today for a detailed evaluation and to start your customised Homeopathy medicines for the treatment of low sperm count.
Levels of Oligospermia – Low Sperm Count
In the latest statement of semen quality (2010), the WHO now considers a sperm count of 15 million sperm/ml and lower as low sperm count.
What is a Low Sperm Count?
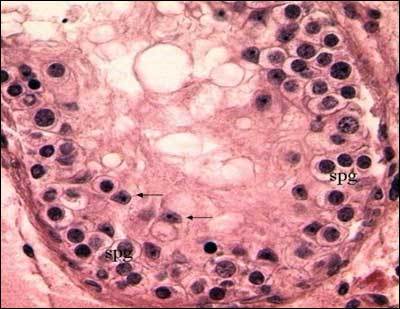
Having a low sperm suggests that it may be difficult to conceive naturally. It does not necessarily mean that it will be harder to conceive. Remember, it takes two to conceive and the health of the female partner matters significantly for conception. In addition, no exact correlation exists between the severity of oligospermia (Table 1) and conception rates. In summary, the most important points about the sperm count and fertility are:
- Reference ranges for sperm counts are defined in fertile (not infertile) men.
- Except when no sperm are found, the sperm count is not a good measure of fertility.
- Many men conceive without trouble having low sperm counts.
Overall Health
A low sperm count can be an indicator of a general medical problem or a genetic condition. In 2% of men, low sperm counts may be due to hormonal imbalance from prolactinoma. In addition, one of the most common causes of low sperm counts is a varicocele. Increasingly, genetic abnormalities are being found in men with severe oligospermia. Missing regions on the Y chromosome (microdeletions) occur in 6% of men with low sperm counts and 15% of men with no sperm counts.
In addition, 2% of men with low counts and 15-20% of men with no sperm counts will harbor chromosomal abnormalities detected by cytogenetic analysis (karyotype). These include conditions such as Klinefelter syndrome (47, XXY) and exchanges of genetic material in non-sex chromosomes and are detected by blood tests. It is also important to remember that sperm counts are a relatively sensitive measure of overall health.
The consistent use of hot tubs or baths, recreational drugs such as alcohol, cocaine, marijuana or tobacco, and fevers from flu’s or other infections can all lower sperm counts in otherwise healthy men. Chronic stress from sleep disorders, travelling, or from work or emotional issues can also lower sperm counts. Generally, their effects are reversible upon recovery.
The main sign of low sperm count is the inability to conceive a child. Often, there are no other obvious signs or symptoms. In some cases, however, an underlying problem such as an inherited hormonal imbalance or a condition that blocks the passage of sperm may cause signs and symptoms. Low sperm count symptoms may include:
- The inability to conceive a child
- Problems with sexual function — for example, low sex drive or difficulty maintaining an erection (erectile dysfunction)
- Pain, swelling or a lump in the testicle area
- Decreased facial or body hair or other signs of a chromosome or hormone abnormality
Causes of Oligospermia ( Low Sperm Count )
Sperm production is complex and requires normal functioning of the testicles (testes) as well as the hypothalamus and pituitary glands — organs in your brain that produce hormones that trigger sperm production. Once sperm are produced in the testicles, delicate tubes transport them until they mix with semen and are ejaculated out of the penis. Problems with any of these systems can affect sperm production. In addition, a number of issues can cause abnormal sperm shape (morphology) or movement (motility). Often the cause of low sperm count isn’t ever identified.
Medical causes
Low sperm count can be caused by a number of health issues and medical treatments. Some of these include:
- Varicocele. A varicocele is a swelling of the veins that drain the testicle. This may prevent normal cooling of the testicle, leading to reduced sperm count and fewer moving sperm.
- Infection. Some infections can interfere with sperm production and sperm health or can cause scarring that blocks the passage of sperm. These include some sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), including chlamydia and gonorrhea; inflammation of the prostate (prostatitis); inflamed testicles due to mumps (mumps orchitis); and other infections of the urinary tract or reproductive organs.
- Retrograde ejaculation. This occurs when semen enters the bladder during orgasm instead of emerging out of the tip of the penis. Various health conditions can cause retrograde ejaculation, including diabetes, multiple sclerosis, spinal injuries, and surgery of the bladder, prostate or urethra. Retrograde ejaculation can also be caused by certain medications — particularly medications for enlarged prostate, such as terazosin (Hytrin), tamsulosin (Flomax) and alfuzosin (Uroxatral).
- Lack of ejaculation. Some men with spinal cord injuries or certain diseases can’t ejaculate semen, even though they still produce sperm.
- Antibodies that attack sperm. Anti-sperm antibodies are immune system cells that mistakenly identify sperm as harmful invaders and attempt to eliminate them. This is especially common in men who’ve had a vasectomy.
- Tumors. Cancers and nonmalignant tumors can affect the male reproductive organs directly, or can affect the glands that release hormones related to reproduction (such as the pituitary gland). In some cases, surgery to treat tumors can affect male fertility.
- Undescended testicles. In some males, during fetal development one or both testicles fail to descend from the abdomen into the sac that usually contains the testicles (scrotum).
- Hormone imbalances. Infertility can result from disorders of the testicles themselves or an abnormality affecting the glands in the brain that produce testosterone and other hormones that control the testicles (the hypothalamus or pituitary glands). Low testosterone (male hypogonadism) and other hormonal problems have a number of possible underlying causes.
- Sperm duct defects. The tubes that carry sperm can be damaged by illness or injury. Some men are born with a blockage in the part of the testicle that stores sperm (epididymis) or a blockage of one of the tubes that carry sperm out of the testicles (vas deferens). Men with cystic fibrosis and some other inherited conditions may be born without sperm ducts altogether.
- Chromosome defects. Inherited disorders such as Klinefelter’s syndrome — in which a male is born with two X chromosomes and one Y chromosome instead of one X and one Y — cause abnormal development of the male reproductive organs.
- Problems with sexual intercourse. These can include trouble keeping or maintaining an erection sufficient for sex (erectile dysfunction), premature ejaculation, painful intercourse, or psychological or relationship problems that interfere with sex.
- Celiac disease. A digestive disorder caused by sensitivity to gluten, celiac disease can cause male infertility. Fertility may improve after adopting a gluten-free diet.
- Certain medications. Testosterone replacement therapy, long-term anabolic steroid use, cancer medications (chemotherapy), certain antibiotics, some ulcer medications and certain other medications can impair sperm production and decrease male fertility.
Environmental Causes of Low Sperm Count
Overexposure to certain environmental elements such as heat, toxins and chemicals can reduce sperm production or sperm function. Specific causes include:
- Pesticides. Some men exposed to pesticides such as ethylene dibromide and organophosphates have lowered sperm counts. Pesticide exposure has also been linked to testicular cancer. Most studies have been done on men who work in agriculture or live in agricultural areas.
- Heavy metal exposure. Exposure to lead or other heavy metals also may cause infertility.
- Exposure to radiation or X-rays. Exposure to radiation can reduce sperm production. It can take several years for sperm production to return to normal. With high doses of radiation, sperm production can be permanently reduced.
- Overheating the testicles. Frequent use of saunas or hot tubs may temporarily lower your sperm count. Sitting for long periods or wearing tight clothing also may increase the temperature in your scrotum and reduce sperm production.
- Prolonged bicycling. Prolonged bicycling is another possible cause of reduced fertility due to overheating the testicles. In some cases, bicycle seat pressure on the area behind the testicles (perineum) can cause numbness in the penis and erectile dysfunction.
Health, lifestyle and other causes
Some other causes of low sperm count include:
- Illegal drug use. Anabolic steroids taken to stimulate muscle strength and growth can cause the testicles to shrink and sperm production to decrease. Use of cocaine or marijuana may temporarily reduce the number and quality of your sperm as well.
- Alcohol abuse. Heavy drinking can lower testosterone levels, cause erectile dysfunction and decrease sperm production. Liver disease caused by excessive drinking may also cause fertility problems.
- Tobacco smoking. Men who smoke may have a lower sperm count than do those who don’t smoke. Secondhand smoke also may affect male fertility.
- Emotional stress. Stress may interfere with certain hormones needed to produce sperm. Your sperm count may be affected if you experience severe or prolonged emotional stress. A problem with fertility itself can sometimes become long term and discouraging, producing stress.
- Vitamin deficiency. Deficiencies in nutrients such as vitamin C, selenium, zinc and folate may contribute to decreased sperm production and male infertility.
- Weight. Obesity can cause hormone changes that reduce male fertility. Men who are underweight also may have reduced fertility.
- Age. Men older than 35 begin to have a gradual decline in sperm production.
- Incomplete sperm collection. Lower than normal sperm counts can result from testing a sperm sample that was taken too soon after your last ejaculation; was taken too soon after an illness or stressful event; or didn’t contain all of the semen you ejaculated because some was spilled during collection. For this reason, results are generally based on several samples taken over a period of time.
Risk factors For Oligospermia ( Low Sperm Count )
A number of risk factors are linked to low sperm count and other problems that can cause low sperm count. They include:
- Being age 35 or older
- Smoking tobacco
- Abusing alcohol
- Using certain illegal drugs
- Being overweight
- Being underweight
- Having certain past or present infections
- Being exposed to toxins
- Overheating the testicles
- Having a prior vasectomy or vasectomy reversal
- Being born with a fertility disorder or having a blood relative with a fertility disorder
- Having certain medical conditions, including tumors and chronic illnesses
- Undergoing medical treatments, such as surgery or radiation for cancer
- Taking certain medications
- Bicycling for long periods, especially on a hard seat or poorly adjusted bicycle
Low Sperm Count and Risk of Cancer
Low sperm counts can also mean that a patient is at higher risk of developing both testicular cancer (2.8x higher) and prostate cancer (2.6x higher) later in life. In this sense, then, a low sperm count can be a natural biomarker of future health in men.
For these reasons, all infertile men with a low sperm count should be evaluated with a thorough history and physical examination by a specialist. This assessment should also include a measure of the pituitary-gonadal hormones testosterone, FSH and prolactin. After this, it is not uncommon to prescribe lifestyle changes, offer medical therapy to correct and improve sperm counts and augment natural fertility.
How To Increase Low Sperm Count ?
Oligospermia is diagnosed if sperm is with a low concentration of sperm and is a common finding in male infertility. The treatment for low sperm count depends on the cause, which can be either genetic or environmental. Genetic causes include Y chromosome microdeletions, Klinefelter syndrome, cystic fibrosis, spinal cord injury, testicular torsion, varicocele, cryptorchidism, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, androgen insensitivity syndrome, and idiopathic oligozoospermic men.
Environmental factors that may lead to decreased spermatogenesis are smoking, alcohol consumption, obesity, exposure to pesticides, radiation, chemotherapy, and certain medications such as anti-androgens, glucocorticoids, anticonvulsants, and chemotherapeutic agents.
Homeopathy Medicines for Low Sperm Count
You can visit Welling Clinic for a complete detailed evaluation of the sperm count and the causation. Welling Clinic offers custom-made natural Homeopathic medicines for the treatment of Oligospermia – low sperm count.
Call +91 8080 850 950 to book an appointment or consult & order online. Consult our specialists today for a detailed evaluation and to start your customised Homeopathy treatment of low sperm count.
